Meta’s Next Big Move: The Future of Virtual Reality

Virtual reality has long been seen as the next big leap in digital experiences. While it has made strides in gaming and simulations, its full potential is only now beginning to emerge. Meta, the company formerly known as Facebook, has been positioning itself at the center of this VR evolution. With the rebranding to Meta and its focus on building the “metaverse,” the company has invested billions in reshaping how we live, work, and interact through immersive technology. But what exactly is Meta’s next big move, and how might it impact the future of virtual reality?
Meta’s Vision of the Metaverse
Meta envisions the metaverse as a fully immersive, 3D internet where people can interact with others, conduct business, attend events, or explore virtual worlds as digital avatars. This isn’t just about playing games; it’s about creating a new dimension of life online. Meta CEO Mark Zuckerberg has described the metaverse as the “next chapter for the internet,” where presence and connection are more real than ever before.
To support this vision, Meta has launched a range of products and platforms. Horizon Worlds is one of its flagship social VR platforms, where users can create and explore custom-built environments. Meta has also introduced work-focused solutions like Horizon Workrooms, aiming to replace video calls with virtual meetings in shared 3D spaces. While the idea is still in its early stages, these platforms are already showing what’s possible in the coming years.
Investments in Hardware and Software
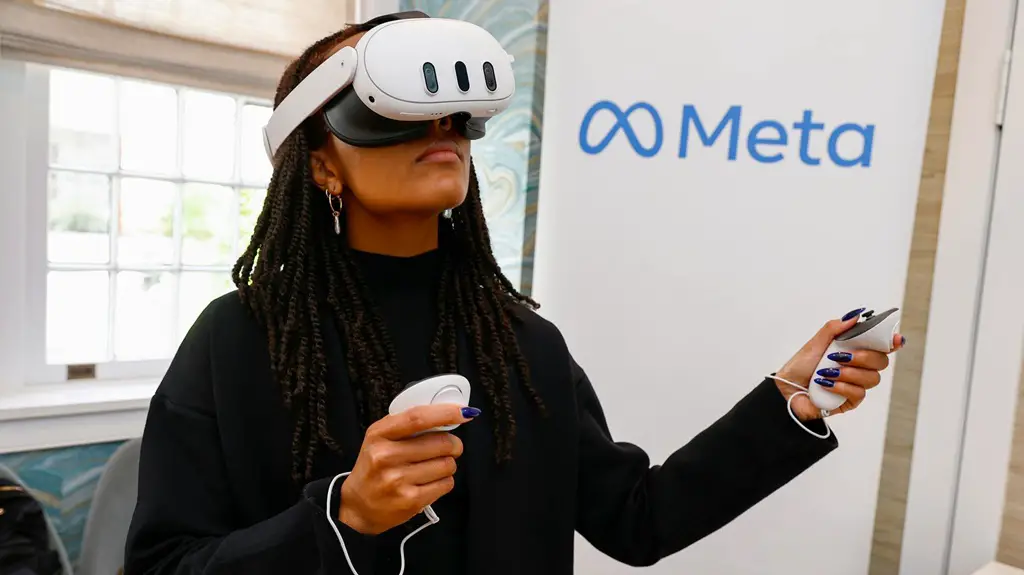
Meta’s success in the VR space largely depends on its ability to deliver seamless, high-quality hardware. The company’s Quest series of VR headsets has been at the forefront of consumer-grade virtual reality. The latest in this line, the Quest 3, includes mixed reality capabilities that combine VR with AR (augmented reality), making the experience more immersive and interactive.
The company is also working on high-end devices like the Meta Quest Pro, aimed at professionals and developers who need more powerful tools. These headsets are expected to offer better graphics, eye tracking, facial expression recognition, and enhanced comfort for long-term use. This move suggests that Meta is not only targeting casual users but also enterprise applications, education, and creative industries.
On the software front, Meta has opened up its ecosystem to developers, encouraging them to build VR experiences and tools for the metaverse. Its development tools are designed to make it easier for creators to produce rich, interactive environments. This is crucial, as content will be the lifeblood of the metaverse. Without engaging and useful VR environments, users won’t stay.
Challenges Meta Faces
Despite its grand vision, Meta faces several challenges. First is the issue of user adoption. While VR technology has come a long way, it still requires relatively expensive hardware and a learning curve that not all consumers are ready for. Many people still view VR as a novelty, rather than a daily utility.
There are also technical hurdles to overcome. VR needs high-resolution displays, powerful processors, and fast, low-latency internet connections to deliver a smooth experience. For the metaverse to truly take off, infrastructure improvements are necessary, particularly in regions with slower connectivity.
Privacy and security are additional concerns. As users spend more time in virtual environments, their behavior, movement, and even biometric data could be tracked. Meta, which has faced repeated criticism over its handling of personal data, must build trust in its new platforms. Users need assurance that their virtual lives won’t be exploited for advertising or surveillance.
Lastly, competition is growing. Companies like Apple, Microsoft, Google, and others are all investing in mixed and virtual reality. Apple’s Vision Pro headset, for example, is expected to redefine how we interact with digital content through spatial computing. Meta will have to innovate quickly and consistently to maintain its leadership.
Real-World Applications and the Road Ahead
Meta’s metaverse ambitions go beyond games and social experiences. The company is exploring practical applications in fields like education, healthcare, design, and remote work. Virtual classrooms could allow students from different countries to learn together. Architects and designers could collaborate in shared 3D environments. Therapists might use VR to treat anxiety or PTSD through exposure therapy in controlled virtual spaces.
Work is another focus area. Meta believes the metaverse could eventually replace traditional offices with fully virtual workspaces. Instead of commuting or sitting on a video call, employees could meet in a shared digital environment, complete with virtual whiteboards, avatars, and natural communication cues.
Entertainment will also evolve. Meta is investing in VR concerts, sports, and events where users can feel like they’re really there. This level of presence could redefine the idea of online experiences, making them more social and emotionally engaging.
The next few years will be critical. Meta’s future—and perhaps the future of VR itself—depends on the ability to deliver meaningful, accessible, and ethical virtual experiences. With its massive investments, developer ecosystem, and hardware innovation, Meta is in a strong position. But success will depend not just on technology, but on adoption, trust, and creativity.
Conclusion
Meta’s next big move is a bold one. The company wants to build a new version of the internet—one where virtual reality isn’t just an add-on but a central way of experiencing the digital world. It’s an ambitious plan filled with opportunities and challenges. If it succeeds, Meta could redefine how we live, work, and connect in a world where physical limits no longer apply. As the metaverse unfolds, all eyes will be on how Meta brings its virtual vision to life.